Ethyl Acetate H Nmr. Not only is it able to give you information regarding which functional groups are present, but nmr spectra are also capable of giving information about the positions of atoms in the molecule. Overview of 1h nmr spectrum of ethyl acetate nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (nmr) is a type of absorption spectroscopy.
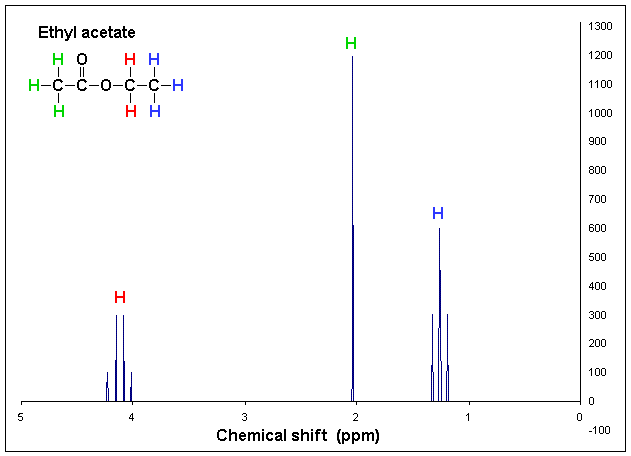
The ethyl acetate, so that you can compare the number of molecules present, not just the number of h in each molecule. Spectra of ethyl acetate 1h nmr spectrum triplet d ~ 1.3 ppm ; Spectra of ethyl acetate 1 h nmr spectrum.
Acetonitrile, Diglyme, Dioxane, Hmpa, Pyridine.
Singlet d ~ 1.9 ppm ; Click the 2d protons and the coloured spectrum peaks to view the respective 3d models. Molecular formula c6h10o3 molecular weight 130.14.
Galli, C., Gentili, P., And Guarnieri, A.
Assigned to ch 3 part of ethyl group, triplet splitting due to neighbouring ch 2.; Ethyl acetate is the acetate ester formed between acetic acid and ethanol. Nmr chemical shifts of common laboratory solvents as trace impurities hugo e.
Here Is An Example Where Nmr Can Be Used To Distinguish
There is a quartet and a triplet; 379.88 4.242 52 372.75 4.163 171 365.56 4.082 180 358.50 4.003 62 182.56 2.039 1000 119.69 1.337 245. Assigned to ch 3 part of acetyl (ethanoyl) group, no splitting as no hydrogens attached to adjacent carbon ;
1H Nmr Data Proton Mult Cdcl 3 (Cd 3) 2Co (Cd 3) 2So C 6D 6 Cd 3Cn Cd 3Od D 2O Solvent Residual Peak 7.26 2.05 2.50 7.16 1.94 3.31 4.79 H 2O S 1.56.
Introduction to nmr chem 117 the chemical shift now, i'll show you some spectra, and explain everything by example. This video is about the basics tips that can be learned to predict proton nmr spectral graph of any compound. Triplet d ~ 1.3 ppm ;
By Summing Up The Building Blocks And Taking Into Consideration The Functionality Suggested By The Molecular Formula And Chemical Shifts, It Is Inferred That Compound 1 Is Ethyl Acetate.
Assigned to ch3 part of acetyl (ethanoyl) group, no splitting as no hydrogens attached to adjacent carbon Then, the interaction of electromagnetic radiation in the radio frequency region with the nuclei of the molecules is recorded. Protons in chemically equivalent environments appear in the same place of the spectrum.
Related Posts
- Sodium Acetate Lewis StructureSodium Acetate Lewis Structure. Isoflex topas nb 52 and isoflex topas nb 152 are rolling and plain bearing greases based on a synthetic hydrocarbon o ...
